Data Flow
The Elasticsearch flow is one way, it will only ever receive data from Lycan. Once configured, the flow for property data getting to Elasticsearch is as follows:
- Property on Lycan receives an update via API request from a connected integration (such as a PMS)
- Lycan will then merge this update to any listings internally that meet its criteria.
- A changeset will be calculated to determine if any changes have been made.
-
- If no changes have been made then Lycan will stop execution.
- If changes are made, Lycan will add the property schema to the Elasticsearch batch queue.
- Periodically, the batch queue will be flushed to update the properties on the configured Elasticsearch instance.
Schema Changes
You can view the Elasticsearch mapping schema here:
https://github.com/aptenex/lycan-elasticsearch-config/blob/master/src/property-mapping.json
These are changes you need to be aware of when querying data and returning it the user.
In any object where description contains a locale => description object it will be converted into an array of description objects instead. Eg:
{
"description": {
"en": {
"locale": "en",
"title": "Example",
"content": "content 123"
}
}
}
to
{
"description": [
{
"locale": "en",
"title": "Example",
"content": "content 123"
}
]
}
Configuring Lycan
Lycan stores two different pieces of data about Elasticsearch, it’s overall instance details (the host) and each index.
Configuring an ES Host
We will setup the host instance for you on Lycan, get in touch with your integration manager.
Configuring an index
Each Elasticsearch index will be attached to a channel connection, if you are pushing to eg. HomeAway, Airbnb and a custom website then you will only need to configure an index on the custom website.
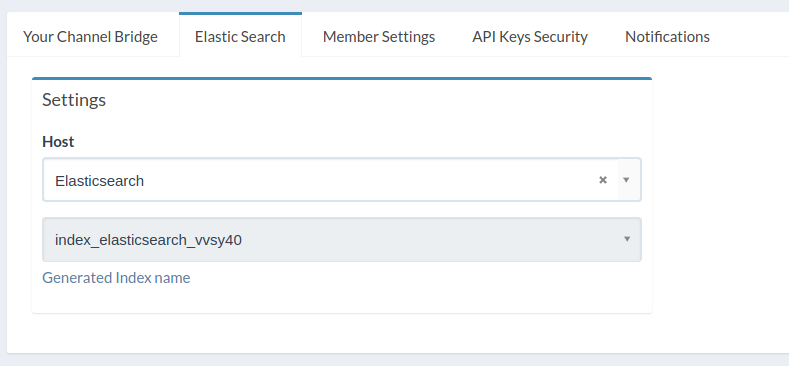
Pushing data to ES
On the Elasticsearch tab now click “Push All Properties” to to populate ES with the property documents. After that has completed you’ll be able to query ES directly using their RESTful API interface.